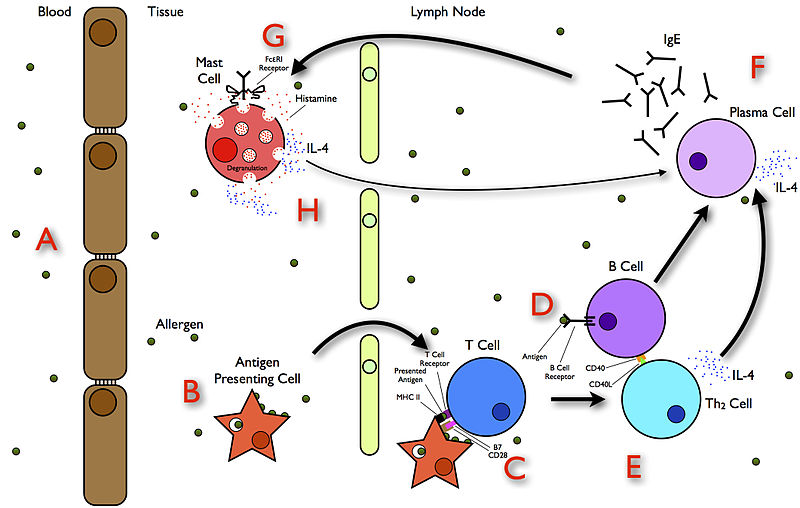
English: Simplified diagram showing key events that leads to allergy initiation.
A. the allergen enters the body.
B. an
Antigen-presenting cell takes up the allergen molecule and presents its
epitopes, through the
MHC II receptor, onto its surface. The activated antigen presenting cell then migrates to the nearest lymph node
C. where it activates T cells that recognize the allergen. They then give the decision for the T cell to differentiate to
Th2 cell.
D. at the same time, B cells recognize the allergen and through the activated Th2 cell
E. the B cell would be activated.
F.and differentiate into plasma cells, at which point they would actively synthesize antibodies of the
IgE isotype.
G. the IgE antibody, that now recognizes epitopes of the allergen molecule, circulates around the body through the
lymphatic and
cardiovascular systems and finally binds to its
FcεRI receptor on mast and basophil cells.
H. when the allergen re-enters the body at a later time it binds to the IgE, which is on the cell surface, resulting in an aggregation of the receptor causing the cells to release pre-formed mediators. One of these mediators is
histamine which causes the 5 symptoms of allergic inflammation: heat, pain, swelling, redness and itchiness. Another mediator is IL-4, which affects more B cells to differentiate into plasma cells and produce more IgE and thus the vicious cycle continues.